During the construction of a private house or arranging a city apartment, it is important to pay special attention to the ventilation system. Many focus on insulation, the strength of the walls or foundation, and this is right, but the neglect of ventilation can turn into serious troubles. The result of insufficient ventilation will be stale air, from which the head will begin to hurt, then gradually on the walls, ceiling and ceilings, condensate will begin to accumulate, mold, and maybe even mushrooms. There is no need to talk about a comfortable and comfortable life in such a stuffy and cheese house, and if you notice the first signs of insufficient ventilation - forever fogging windows, outgoing wallpaper and stuffiness - it is time to take appropriate measures.
Content
Device and principle of operation
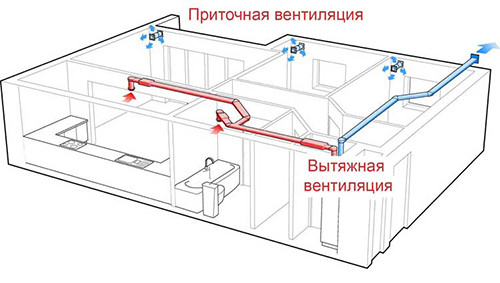
It is not so difficult to make exhaust ventilation with your own hands if you know the principles of its work and use suitable materials. Homemade ventilation systems are relevant for small apartments and private houses. Even if special double -glazed windows with supply valves are installed on the windows, this is not enough - it is necessary to ensure not only the flow of fresh air, but also the removal of spent vapors to the outside. If, on the contrary, make only an output for the exhaust air, then where to get fresh from? Thus, it becomes clear that full -fledged ventilation is possible only in combination with supply and exhaust holes.
The principle of operation of supply and exhaust ventilation is as follows:
- Fresh air from the street penetrates into the house through the influx. This can be carried out both in a natural and in a compulsory way. In the first case, the air enters the supply pipe due to the temperature difference outside and inside the house, as well as due to gusts of wind. This is not the most reliable way, because it does not allow you to control the volume of pure air masses. To do this possible, they organize a forced system that works at the expense of special fans. They suck the air from the street and pour it into the room in the required volume.
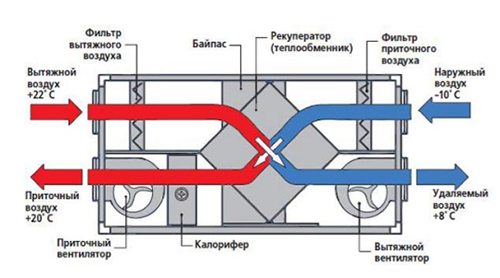
- Once in the supply hole, fresh air passes the filtration system, if filters are installed, heated if there is heating equipment. Heating occurs in a recuperator, about the advantages of the installation of which we will talk a little later.
- Next, the cleaned and heated flow goes through the air duct and enters the room.
- At the same time, the exhaust air heats up and, according to the laws of physics, rises up to the exhaust hole. A natural or mechanical (forced) principle of operation can also be used here. In the latter case, the air is sucked in a fan, passes through the air duct and pushed out.

The arrangement of forced supply and exhaust ventilation can “fly into a penny”, however, a one-time investment will pay off quite quickly, and then it will save on electricity and heating. The advantages of using such systems include the convenience of operation, absolute safety and efficiency. When the air continuously circulates in the house, residents are much less common and generally feel more vigorous, the life of the walls and ceilings is longer, the laundry dries faster, etc. Thus, by setting ventilation, you contribute to your own health and durability of your housing.
The degree of complexity of the ventilation system directly depends on the volume of the room that needs to be ventilated. In the case of a private house, this is the total volume (not to be confused with the area) of all rooms on all floors.
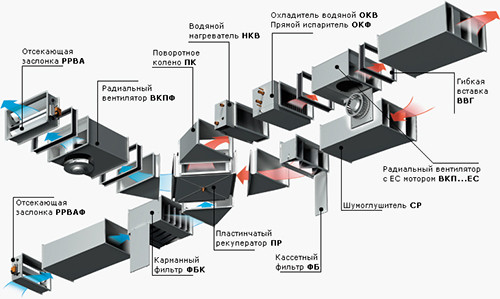
Exhaust ventilation device:
- The supply valve is equipped with a lattice damper, which serves to change the throughput of the element. Through the supply valve, clean air enters from the street to the duct. The part may have primary cleaning filters. It is placed on the side of the house where a strong wind is most often blowing (as a rule, this is the north side).
- The supply fan is a pressure equipment that creates a vacuum in a valve bell, thereby driving the air into the duct.
- The supply pipeline is pipes along which clean air moves inside the house.
- The mixer is a camera associated with external supply air ducts and channels that remove the supply flows from the rooms. The channels are installed only in recirculation systems that take air not only from the street, but also from the inside.
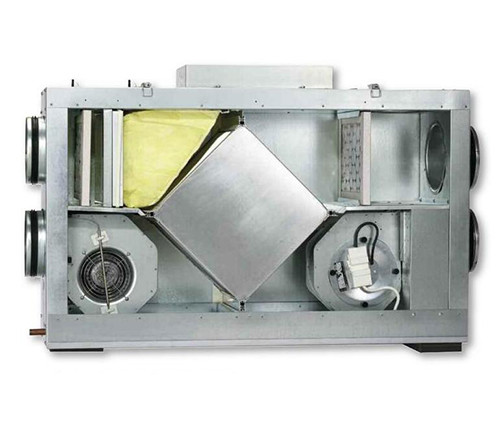
- The recuperator is a special block in which cold air from the street heats up to a comfortable temperature. The operation of the device occurs so that the supply flow is not mixed with exhaust - they pass through separate channels inside the recuperator, as you can see in the diagram below. The supply cold air is heated due to the heated worked out, output. As a result, you save a significant amount of electricity to heating the premises.
- Air conditioning is a device that cools hot air air in a hot season.
- Calorifier - a special device for heating the supply flow. Allows you to unload the main heating system in the winter season. An alternative to a recuperator, but unlike him, the calorifer does not take heat from the exhaust air, but consumes electricity to heat cold flows from the street.
- The collector is a distribution compartment in which the supply flow is distributed into air ducts going to different rooms.
- Expitable diffusers - lattices built into the ceiling or upper part of the walls. They take the spent air out of the rooms.
- Exhaust fans - they are built into the channels of the hoods to create discharge and pressure.
- The air ducts leading from diffusers to a recuperator, where heat is made from spent air and transfer it to a cold stream from the street.
- The central ventilation pipeline is a pipe that is displayed to one level with the roof skate. A spent stream passes along it and is displayed.
As you have already understood, the installation of such a complex system with the presence of all nodes requires professional knowledge and skills, so it is better to entrust the installation to specialists. With your own hands, you can make a simpler exhaust ventilation system, but with a similar principle of operation.
Recuperator
Above, we have already hinted a couple of times on the advantages of using the recuperator when arranging ventilation in the house. We offer to consider this item in more detail. In the process of mixing supply and exhaust ventilation, large loss of efficiency occur. Recovery allows you to increase the efficiency by 10-15% and spend energy as economically as possible.
The principle of operation of the recuperator is very simple: the spent airy masses leave the room and fall into a special heat exchanger, where they give their heat to the supply air moving near the neighboring duct. The most popular companies that offer such energy -saving systems are Daikin and Mitsubishi Electric, but the cost of their products will frighten any economical host. Therefore, an alternative option is brewing itself - why not make a recuperator with your own hands?
The simplest plate design is considered the simplest. Even a beginner can cope with its manufacture. Such a homemade recuperator consists of plates that can be made of thick foil, leaf copper, aluminum, textolite, etc. The device consists of several cassettes, each of which is an equal number of plates. Thus, the number of plates depends on the number of cassettes (about 4 m² of plates takes one cassette). If you want to immediately make a recuperator with a high efficiency, place a doubled number of plates in one cassette.
Tools and materials necessary for the manufacture of a recuperator for exhaust ventilation at home with your own hands:
- steel corners for attaching flanges with racks;
- the rack impregnated with the Oliphi for transferring the plates (can be replaced with technical traffic jams);
- plywood or sheet steel 3-4 mm thick;
- mDF panel 20 mm;
- mineral wool or foam for the filter;
- wooden bars 30x30;
- metizes;
- silicone -based sealant;
- scissors for metal.
How to make exhaust ventilation with a recuperator:
- Using scissors for metal, cut the plates for cassettes in the form of squares 30x30 cm. One cassette includes 70 plates.
- On the parallel edges of each square on one side, glue the rack impregnated with olifa. It will provide the necessary ventilation gap between the elements. The length of the rail should correspond to the length of the quadratic edge - 30 cm. Do not glue the last blank. If for the manufacture of the plates you chose a corrugated worm of the minimum thickness, it is not necessary to glue the slats to it - the wavy structure will leave the required gaps.
- Next, glue the details with each other in a special way: smear each subsequent sheet with glue and unfold 90 ° with respect to the previous one. So you get an equal number of ventilation gaps on each side and at the same time they will not intersect with each other. One will flow in cold air, on the other - warm worked out.
- The last plate without a rail will close the cassette.
- In the intervals, pour silicone sealant.
- At the sides of the resulting cassette, attach fasteners for flanges.
- It is very important to set the cassette on the corner (in the form of a rhombus) and fix it in this position. In the process of heat transfer, condensate will appear. Since he has nowhere to go, he will settle on the inner walls of the plates and slide down - into the lower corner of the rhombus. To give a moisture output, you need to make a hole there and insert a drainage pipe there. Check the drainage outlet from time to time and remove the released liquid.
- If the recuperator consists of two or more cassettes, all of them should have the same size and be located so that the corners fit as tightly and hermetically as possible.
- When the cassette is ready, insert it into the box, the frame of which is made of wooden beams, and the sheathing is made of MDF or sheet steel. Cassettes should not hang inside the box, but sit as tight as possible, so try to immediately make its appropriate sizes. Attach a layer of filtering material (foam or minvata) to the inner wall of the box so that clean air from the street passes initial cleaning.
- In the sidewalls of the box at the points located opposite the flange joints on the cassettes, drill holes.
- Install the recovery unit in the guides from the steel corner, fastening them to the walls. This will allow you to remove the cassette for maintenance or repair at any time.
Installation of ventilation
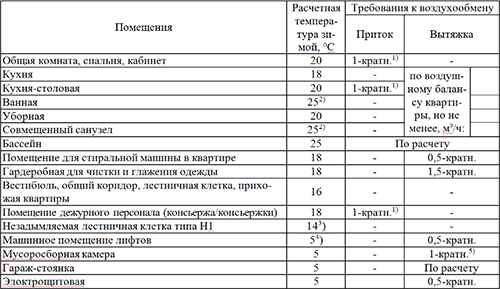
Before accepting the installation of exhaust ventilation, it is necessary to calculate the required volume of clean air, which is needed for all rooms in the house. There are certain air exchange standards for residential premises and they depend on the specifics of the use of a particular room. For example, in the kitchen and in the bathroom, air exchange should be more intense than in the living room or bedroom, because the humidity and speed of air pollution is higher there.
The table below shows the frequency of air exchange in accordance with the purpose of the room:
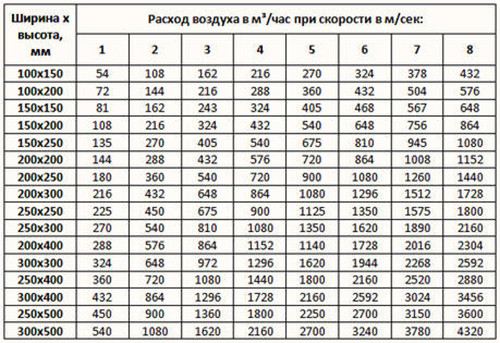
In a residential building for each person, there should be at least 60 cubic meters of fresh air every hour. In the office, this parameter is reduced to 20 cubic meters. The air exchange of industrial premises depends on the characteristics of the working process. For example, if an employee just sits at the computer, he spends less air than the one who works physically. The calculation of air exchange also occurs in accordance with the area of \u200b\u200bthe room: 1 m² should account for 3 m³ of fresh air per hour. If you learn the total volume of supply masses per hour, you can purchase a compressor of appropriate power and performance. Depending on the speed of the air flow, encouraged by the compressor, you can easily calculate the air duct cross section and the number of channels for extract.
The table below shows the dependence of the section of the air duct on the air exchange in the room:
Since the calculation of ventilation is quite complicated, many prefer to entrust this work to specialists, and the installation of equipment is already carried out with their own hands.
The specifics of the installation
The installation of exhaust ventilation should not cause difficulties if you correctly made a calculation and prepared all the necessary components. Each detail should simply be attached using brackets or standard suspensions, and then assemble the air ducts of the desired geometry according to the type of designer. The only difficulty lies not in the assembly, but in creating the project of exhaust ventilation, since it is at this stage that all calculations need to be made.
The sequence of assembly of the ventilation system:
- supply valve;
- recirculation node;
- exhaust and supply collectors;
- recurator/Calorrifice/Air conditioning/filters;
- wiring of exhaust and supply ducts in the manifold;
- grates on supply and exhaust diffusers.
Useful advice: in some areas it is more convenient to use not plastic pipes for ducts, but a corrugation that can bend at any angle and avoids additional connections. To fix the pipe, use standard drywall screws for drywall, screwing them with a “water” after gluing the seam with a sealant.
Remember that the success of the result for the most part depends on the well -compiled exhaust ventilation scheme. If you are uncertained in your abilities or confused when trying to cope with this yourself, it is better to entrust the design of specialists.