Progress cannot be stopped. Every day, our lives include new materials. The revolutionary discovery in terms of laying high -speed communications was the invention of an optical cable.
Content
What is an optical cable
The optical cable is a special genus of cables for communication networks. The main difference from the standard cable is the method of energy transfer. The transmission is carried out using a light flow, and not an electric current at all. By and large, an optical cable is a thread inside which light moves. The main component is optical fiber. It is the most modern and most reliable environment for data transfer. Light along the fibers is transmitted over huge distances with virtually no losses and at high speed.
The main characteristics of the optical cable. Its advantages and disadvantages
The advantage of the optical cable over the usual cable is undoubted. Among the most obvious points I would like to highlight:
- Incredibly high throughput. The optical cable is able to transfer a significant amount of information for a small period of time.
- The fiber does not radiate electromagnetic waves. Accordingly, it is not able to expose electromagnetic radiation. As a result, the signal is protected from distortion.
- The cable is reliably protected from an unauthorized connection. An attempt to unauthorized connection causes a violation of the integrity of the cable and termination of data transfer. It becomes impossible to hide it.
- A very insignificant signal attenuation indicator. Modern fiber of optical cable with a wavelength of 1500 Nm, it has an indicator of attenuation of about 0.3 dB/km. This makes it possible to arrange neighboring repeaters and amplifiers at a distance of up to 100 km.
- The optical cable has less weight and volume than ordinary. For example, the diameter of the 900-part telephone cable is 7.5 cm. It will successfully replace the optical cable with a diameter of about 1.5 cm. Moreover, all kinds of protective shells will be composed of most of the cable. The diameter directly of the fiber will be 0.1 cm.
- When using an optical cable, there is no need to ground the shell. This is due to the insulating properties of fiber.
- The possibility of use at enterprises with increased risk. It is associated with such a feature of fiber as a lack of sparking. It is thanks to her that the optical cable is a fireproof material.
- The optical cable is a very economical material. For the manufacture of fiber, quartz is used, the element is very inexpensive and common. As a result, the cost of the optical cable itself does not differ from the cost of the usual cable.
- Durability. Nothing forever. Over time, all materials, including an optical cable, lose their properties. The attenuation increases. However, these processes occur very slowly. The speed of loss of the properties of the optical cable is much lower in comparison with other types of cables. The term of the uninterrupted operation of the optical cable is at least 25 years.
Despite a large number of positive points, the use of an optical cable has a number of disadvantages:
- The high cost of communications with an optical cable. True, this is due to the use of additional expensive equipment. The cost of the optical cable itself is not too different from the cost of the usual cable.
- The complexity of mounting networks with optical cable. The connectors must be installed literally with micron accuracy. The connection itself must be made very accurately, evenly. The presence of gaps is unacceptable. The surface of the joint must be smoothly polished. In case of non -compliance with the above requirements, losses in the speed and quality of the transmitted signal cannot be avoided.
- The compounds are performed by welding or gluing. When gluing, a special gel is used, which has the same refractive coefficient value as fiberglass.
- In the process of working with an optical cable, special tools are used. The installation of optical networks is carried out exclusively by highly qualified specialists.
- It is possible to spoil the optical cable due to a sharp temperature difference. The fiberglass is cracking. To solve this problem, optical cables are launched into production, in the manufacturing process of which radiation resistant glass is used. Unfortunately, this leads to a significant increase in value.
As you can see, the disadvantages are not so significant. The popularity of optical networks is growing every day. At the same time, the cost of the material is reduced and the number of specialists working with the optical cable is growing. With this trend in the near future, these shortcomings will outline themselves.
Types of optical cables
There are two types of optical cables:
- Single optical cable. All light rays in cables of this type move along one path and at the same time approach the receiver. As a result, there are no distortions of the signal shape. A single -moded cable is equipped with a fiber with a diameter of 1300 nm. Only light waves of the same length are transmitted. The use of single -fashioned cables helps to transmit the signal over more long distances than the use of multi -muddy cables. This feature is associated with very insignificant values \u200b\u200bof dispersion and signal losses. When using a single -fashioned cable, laser LEDs are used. The attenuation of the signal in a single -fashioned cable is very low, about 5 dB/km.
- Multi -doon optical cable. In this type of cable, the rays do not go along one path. Their trajectories have a significant scatter. The result is a distortion of the signal on the receiver. When transmitting a signal through a multi -doon cable, ordinary LEDs are used. This leads to a significant reduction in the cost of communication networks and an increase in the service life of the transceivers. The multi-moded cable is characterized by the length of the light wave of about 850 Nm with deviations of 30-50 nm. The signal attenuation in the cable can reach 20 dB/km. The length of the cable of this type is allowed up to 5 km.
The main type of optical cable is currently multi -fold. This is due to its availability and cheapness. In the future, leading positions should go to the cable to a single -fashioned cable. Its excellent characteristics, the low level of attenuation allow us to hope that over time the high cost of acceptance equipment will cease to be an obstacle to the spread of this high -quality material.
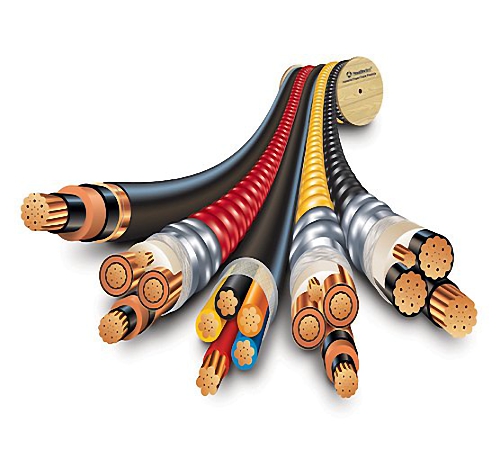
The design of the optical cable
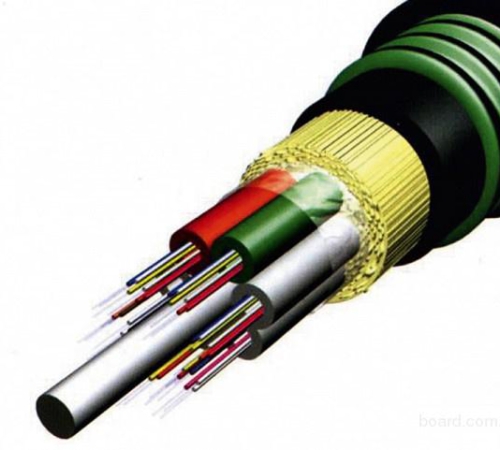
The main components of the optical cable are:
- Optical fiber. A thin glass thread called the core or residential. Coated with a sheath of glass. The coefficient of refraction of the shell is slightly different from the same indicator of the core towards the decrease. That is why the light beam, directed to the core, spreads exclusively on it. Often, to reduce the cost of material, the core is made of plastic, and not from glass. Such optical fibers are worse. Distinguish of single -moded and multi -doon optical fibers. The core of the single -fashioned fiber is very thin, its diameter is about 10 microns. It is precisely because of the insignificant diameter of the core is transmitted only one single fashion for electromagnetic radiation, which excludes the presence of dispersion distortions. But the core of multi -sea fiber is several times thicker, about 50 microns. This contributes to the spread of several mods of radiation on it. Each of the mod spreads at a certain angle. The light impulse is subject to dispersion, which leads to the transformation of its form from rectangular into bell -like.
- Core.
To improve the strength of the optical cable, its optical modules, which are a polymer tube in which the fiber is freely placed, are twisted around the core of the cable.
The role of the core is played by the central power element that protects the structure from the loads.
In the production of optical cables, twisting in layers is used. Twisting elements are concentrically located along the central power element. The purpose of twisting is to achieve the presence of space, within which the load on compression, stretching and bending does not affect the cable transmission. Of course, the maximum value of these loads is limited by certain frames.
Around the central power element, fillers are also stuck. The fillers are:
- Modules without fiber.
- Copper cores
- Plastic rods.
All of the above elements are fastened to each other with a tape or shell. Their combination is called a core.
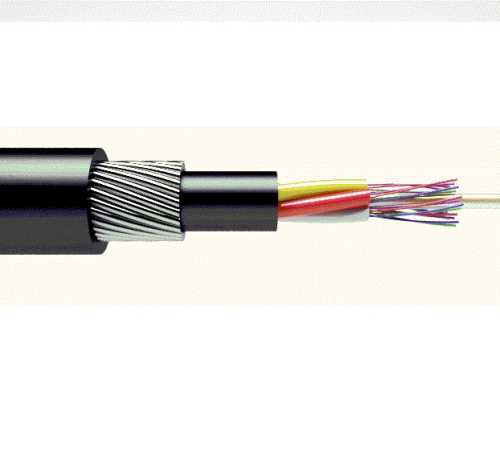
1. Covers for protection and reinforcement. Due to the lack of the need to shield an optical cable from an external electromagnetic obstacle, a metal braid is not used. However, there is a need for the mechanical protection of the cable. For this purpose, the following materials are used:
- kevlar thread;
- steel tape;
- steel wire.
2. The outer shell. It protects the cable from external influences, both mechanical and influences of harmful substances, moisture.
Varieties of cable structures
Distinguish the following varieties of structures:
- Cable for outdoor laying. Purpose - laying in the ground or in the pipe.
The scope of the single -wood - cables with the presence of Neme 10 lights. But with a larger amount of fiber, it is more advisable to use a multi -bearing module or a burning module.
The modules are wrapped in layers along the central power element.
Power elements are covered with a shell made of polyethylene or a layered shell made of polyethylene laminated by aluminum.
The module is filled with a hydrophobic compound.
It is possible to put on the shell of an additional layer of protective armor. In order to protect against pests, corrugated steel ribbons are ideal.
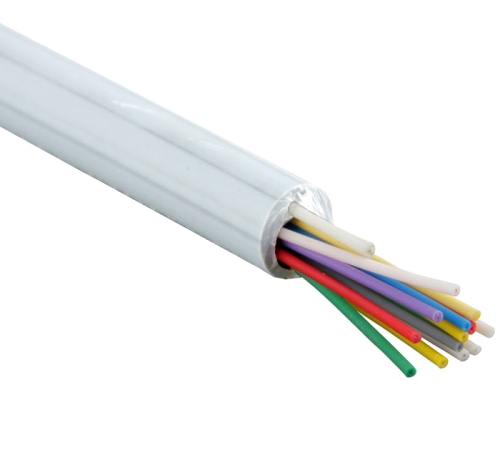
- Cable for internal laying. Used inside buildings. For cables of this species there is no need for grounding, since they do not contain metal. Convenient in use due to lightness and flexibility.
There are cables:
1. Distribution. For individual wiring. Three types of design based on the diameter of the module:
- under severe conditions of use - 0.27 cm;
- under standard conditions of application - 0.24 cm;
- in case of facilitated conditions of application - 0.20 cm.
They are laid in vertical mines inside buildings or in channels located below the level of freezing between neighboring buildings.
2. Connecting. Used as cable jumpers or during the processing process with plug connectors.
3. Special cable. These are universal cables used both outside and inside. Features of an optical cable of this type:
- complete water resistance;
- lack of need for additional fraining at the entrance to the building;
- the presence of special fire requirements.
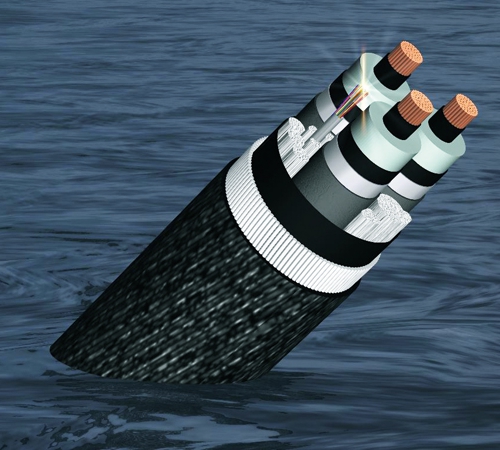
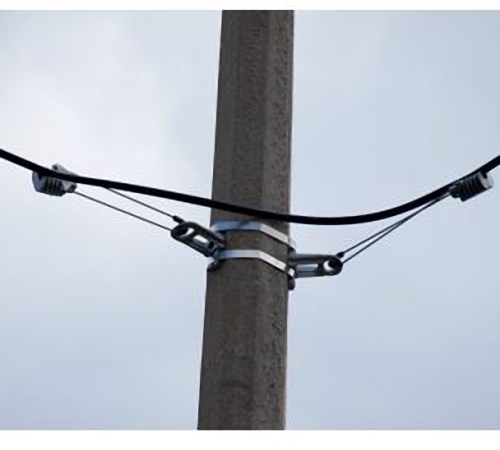
The varieties of special cables are an underwater cable and an optical self -supporting cable, also called air.
Air cables are laid on poles. It can be the pillars of lighting and communication, power lines, electric vehicles. There are a lot of air cables. It all depends on the model. A characteristic feature of the air cable is the high strength of the gap. After all, the load on it is not limited only to its own weight. There is an increase in the load due to icing, wind.
Underwater cables are laid deep under water. The central tube of a cable of this type is made of copper and filled with a hydrophobic gel. But the armor is 2-3 layers of galvanized steel wire. Between the layers and outside is a layer of polyethylene. As a result, the cable feels great at great depths and withstands significant pressure